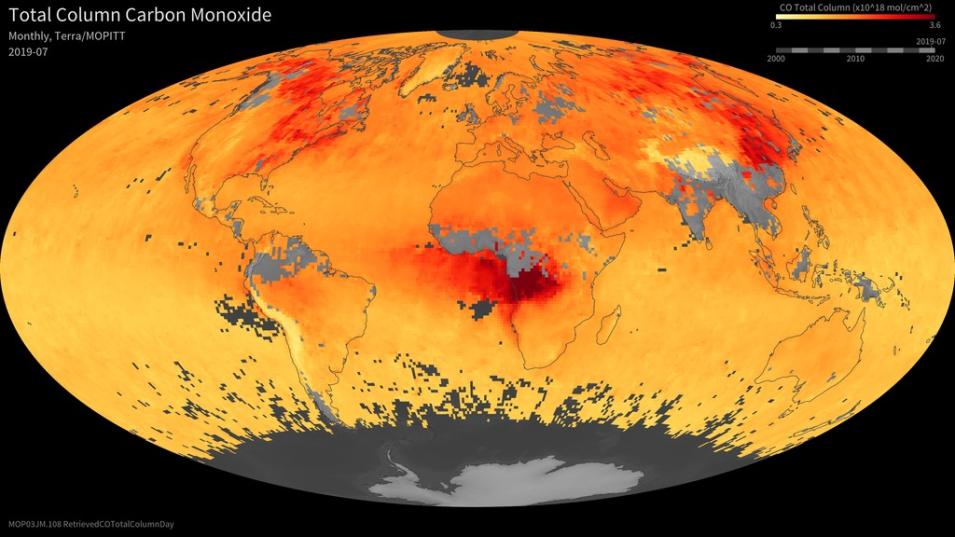
As one of the first satellite instruments to use gas correlation spectroscopy to make Earth observations, NASA’s Measurements Of Pollution In The Troposphere (MOPITT) instrument was a pioneer in collecting air quality data from space. After more than two decades of successful operation, it was retired in early 2025 because the aging Terra satellite it flies aboard no longer generates enough electricity to power the device. The MOPITT subsetter was also deprecated on March 31, 2025.
MOPITT’s specific focus was on the distribution, transport, sources, and sinks of carbon monoxide (CO) in the troposphere. The spectrometer’s marquee Earthdata products have included MOPITT Near Real-Time Datasets and offerings from the MOPITT Science Investigator-led Processing System (MOPITT SIPS).