N: 90 S: -90 E: 180 W: -180
Description
Sentinel-1B, the second satellite in the Sentinel-1 constellation, was launched April 25, 2016. The Sentinel-1 satellites (Sentinel-1A, Sentinel-1B, and Sentinel-1C) are sun-synchronous polar-orbiting satellites that operate day and night performing C-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging. The Sentinel-1 satellites operate in four imaging modes with different resolutions (down to 5 meters) and coverage (up to 400 kilometers). The Sentinel-1 satellites provide dual polarization capability and short revisit times.
The spacecraft experienced an anomaly related to the instrument electronics power supply provided by the satellite platform, leaving it unable to deliver radar data on 23 December 2021, as a consequence, ESA and the European Commission announced the end of the Sentinel-1B mission on August 3, 2022.
Sentinel-1B Single Look Complex (SLC) data products consist of focused SAR data and are provided in slant-range geometry. Slant range is the natural radar range observation coordinate, defined as the line-of-sight from the radar to each reflecting object. The products are in zero-Doppler orientation, where each row of pixels represents points along a line perpendicular to the sub-satellite track.
The products include a single look in each dimension using the full available signal bandwidth and complex samples (real and imaginary) preserving the phase information. The products have been geo-referenced using the satellite’s orbit and attitude data and have been corrected for azimuth bi-static delay, elevation antenna pattern, and range spreading loss.
The data products in this collection mirror the Sentinel-1B products provided through the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem.



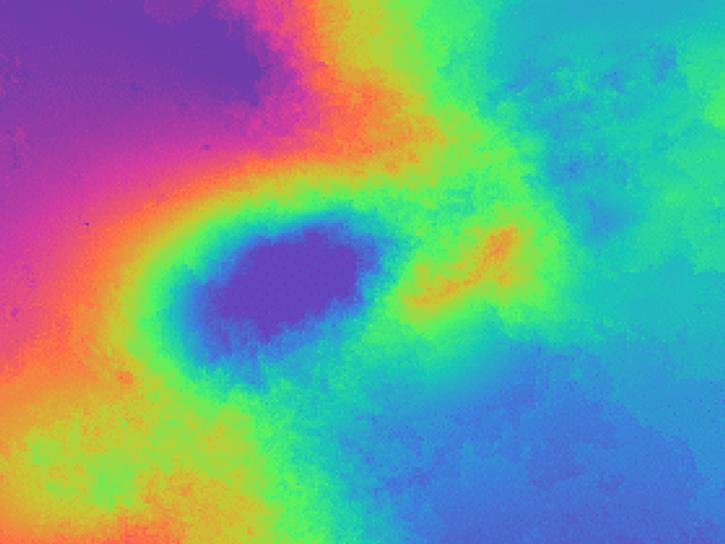
![This image shows Geocoded RGB Composite Image of Bucharest, Romania in Google Earth. Credit: ASF DAAC 2017; Contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data [2015] processed by ESA](https://earthdata.nasa.gov/s3fs-public/styles/hds_generic_card/public/2024-09/rgb-resulting-image.jpg?VersionId=g3VhlSo.o6e0osh0mRBH1pszhjJKgbgX&itok=7pmIc5-N)